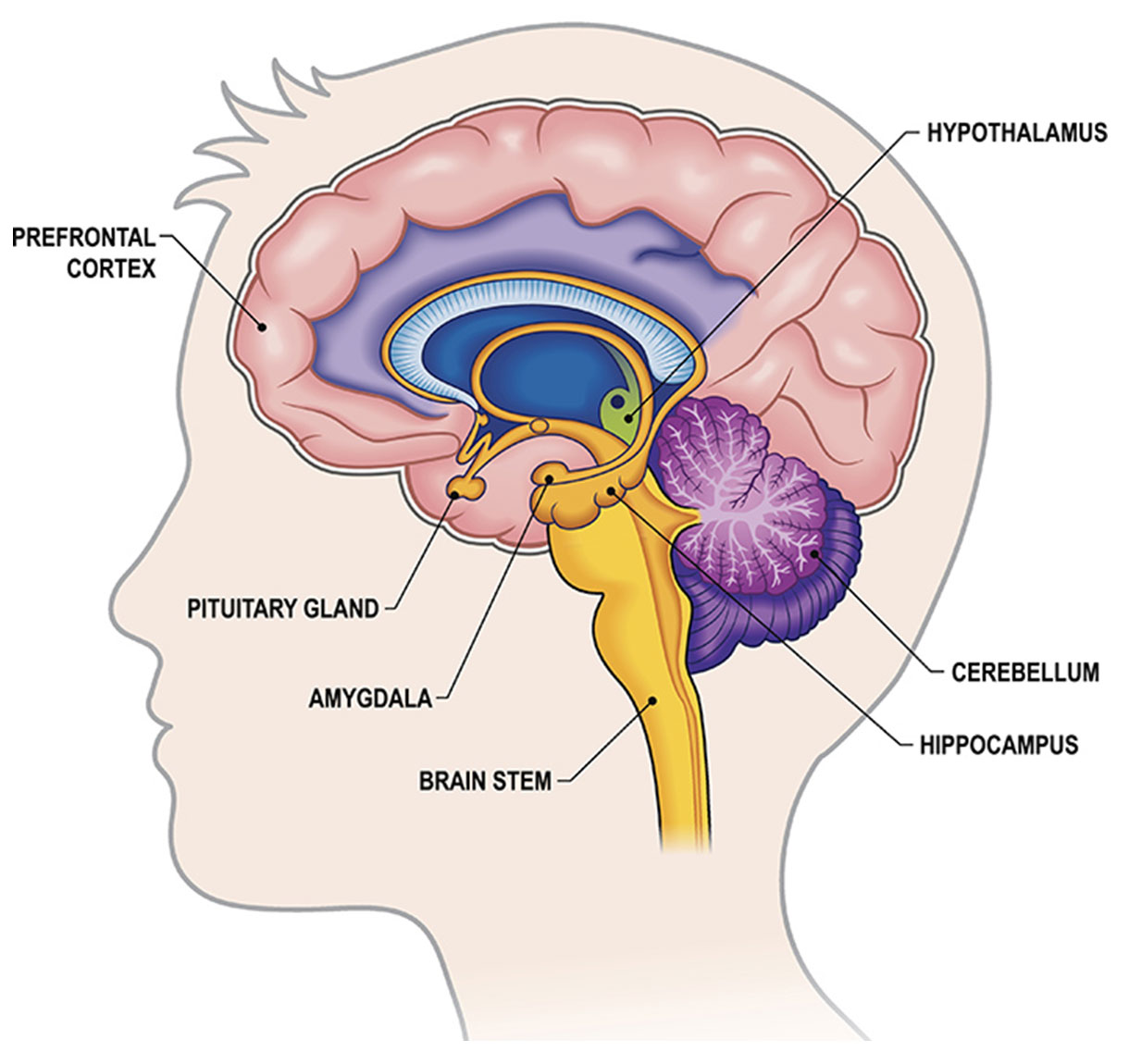
The human brain
Here is a brief overview of neuroanatomy, illustrating the locations in our brains where the conscious and subconscious processes reside.
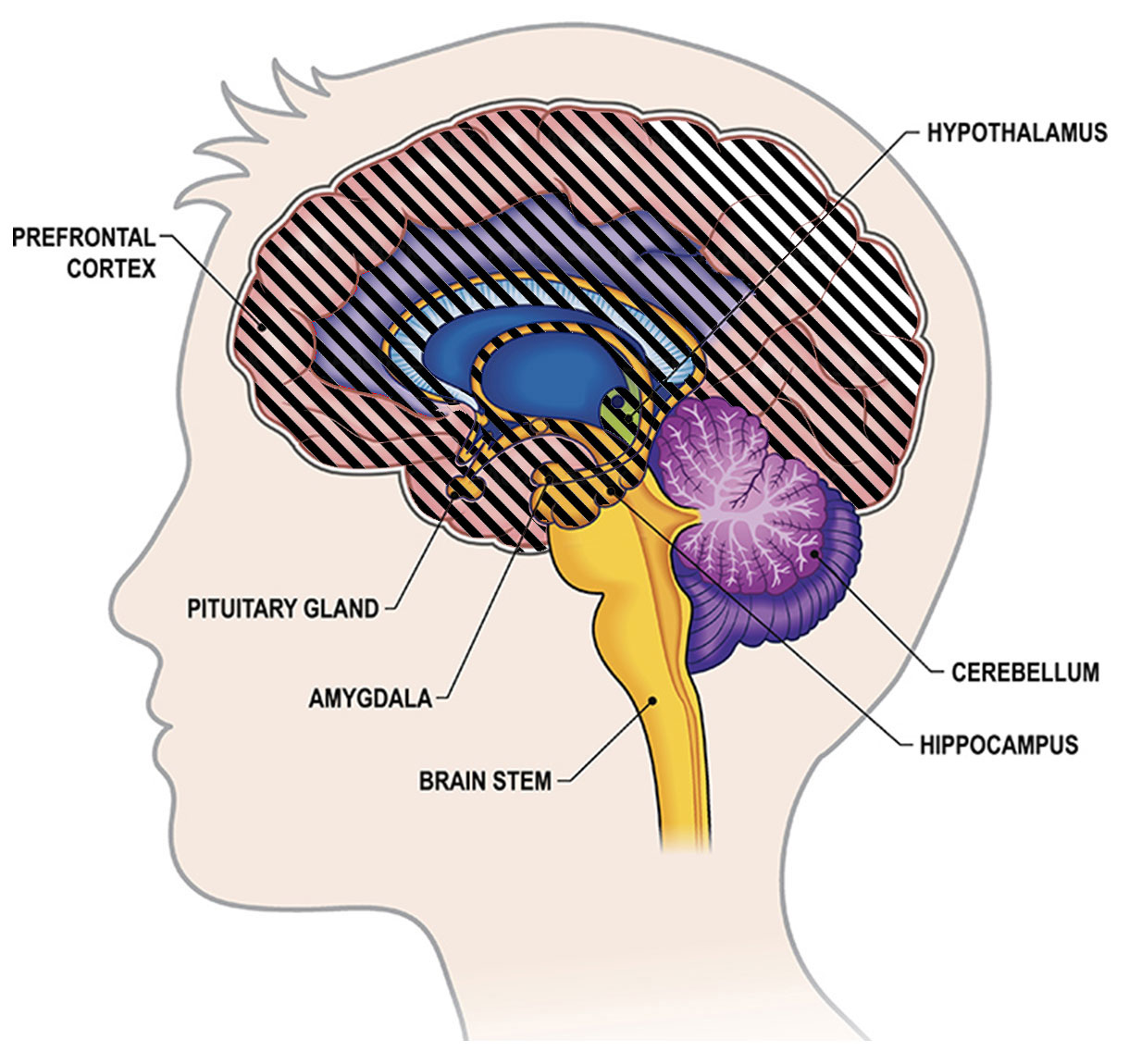
The cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is the largest part of the human brain, comprising 82% of its mass.
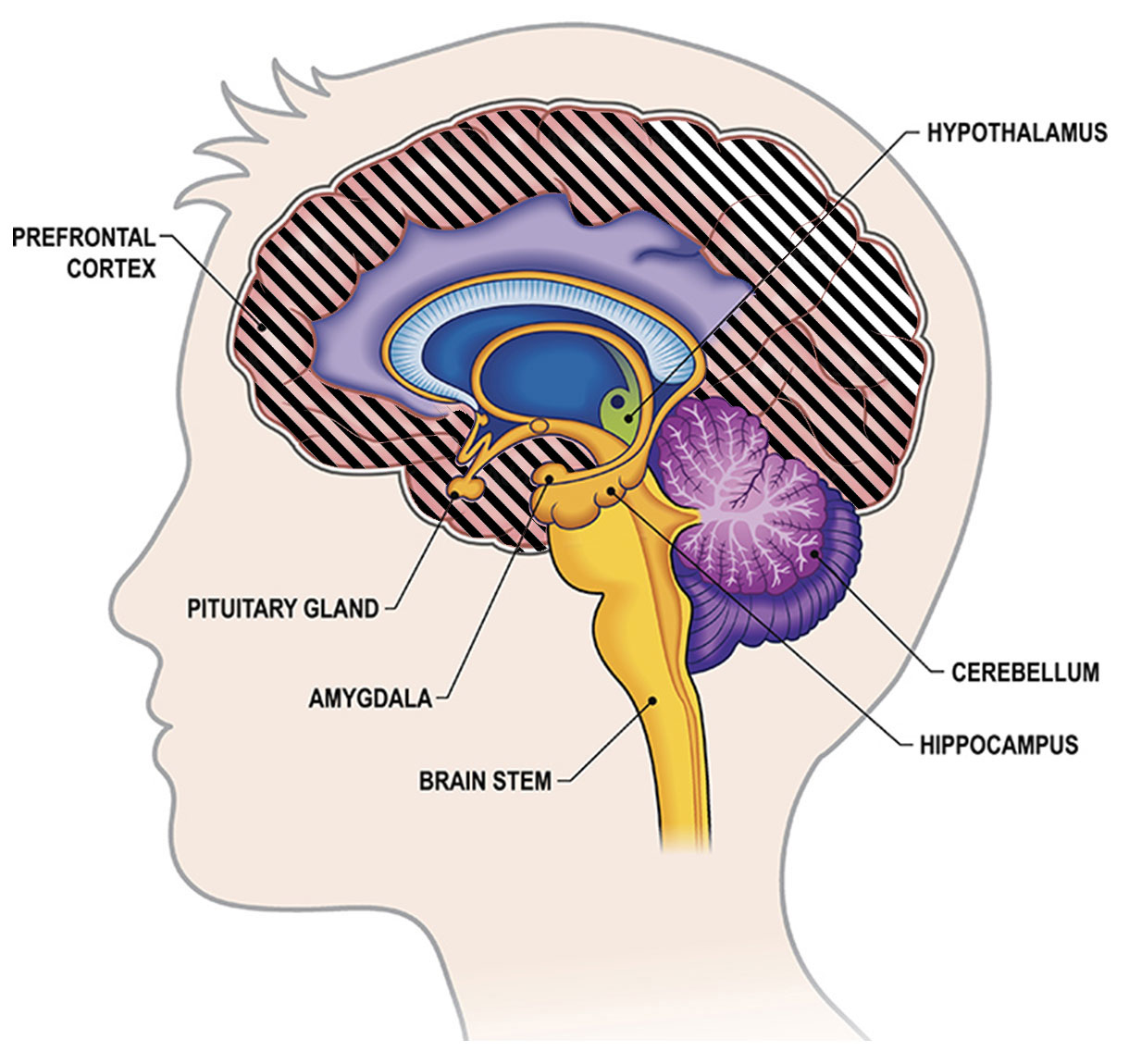
The neocortex
The neocortex comprises the majority of the cerebral cortex, making up about 90% of its total volume.
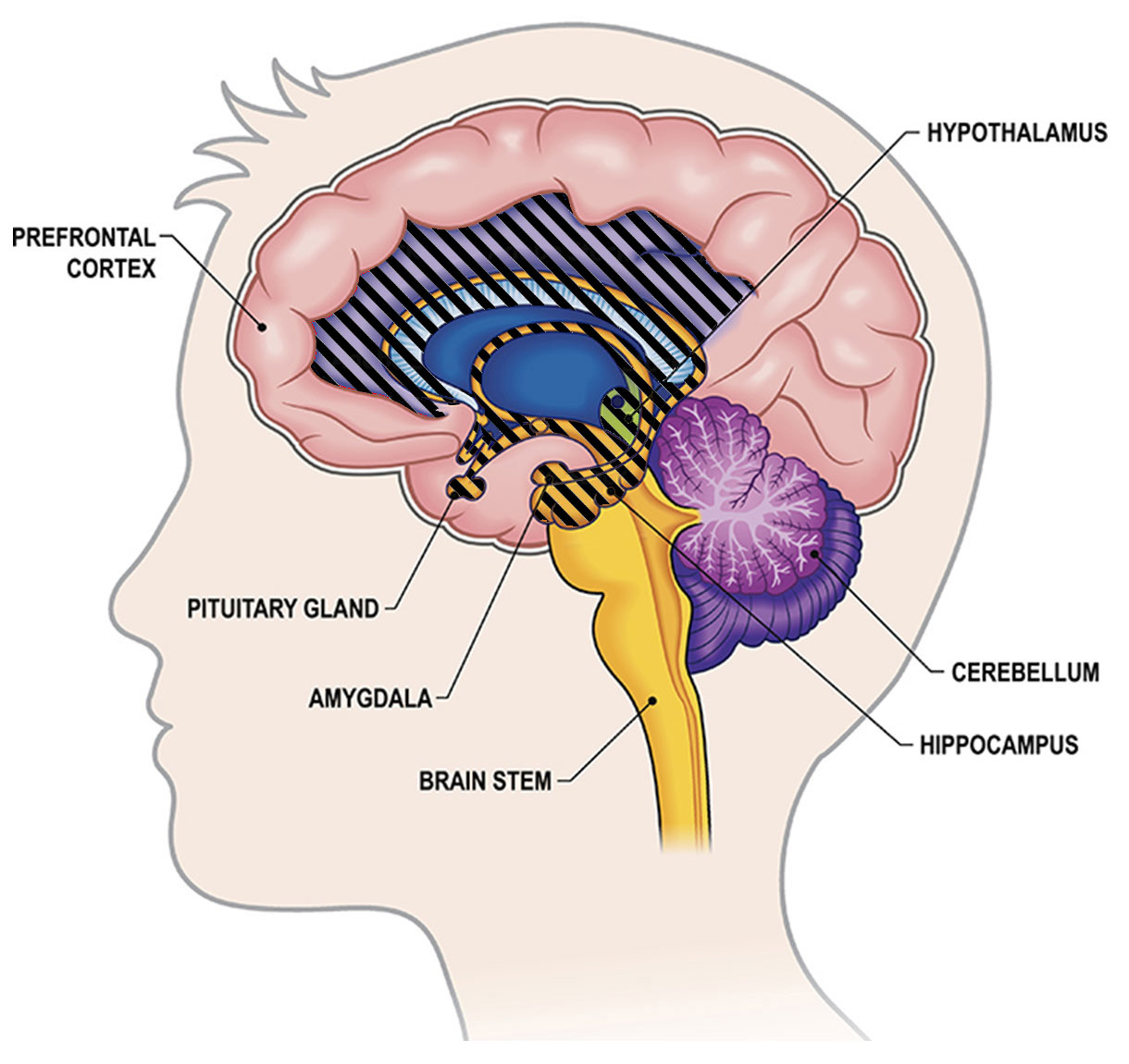
The allocortex
In contrast, the allocortex is a smaller component, constituting roughly 10% of the cerebral cortex.
Most conscious processes take place in the neocortex, which is the outermost layer of the brain responsible for higher cognitive functions such as reasoning and conscious thought.
While the neocortex is heavily involved in many higher-order conscious processes, some aspects of consciousness can involve subcortical (below the neocortex) structures as well.
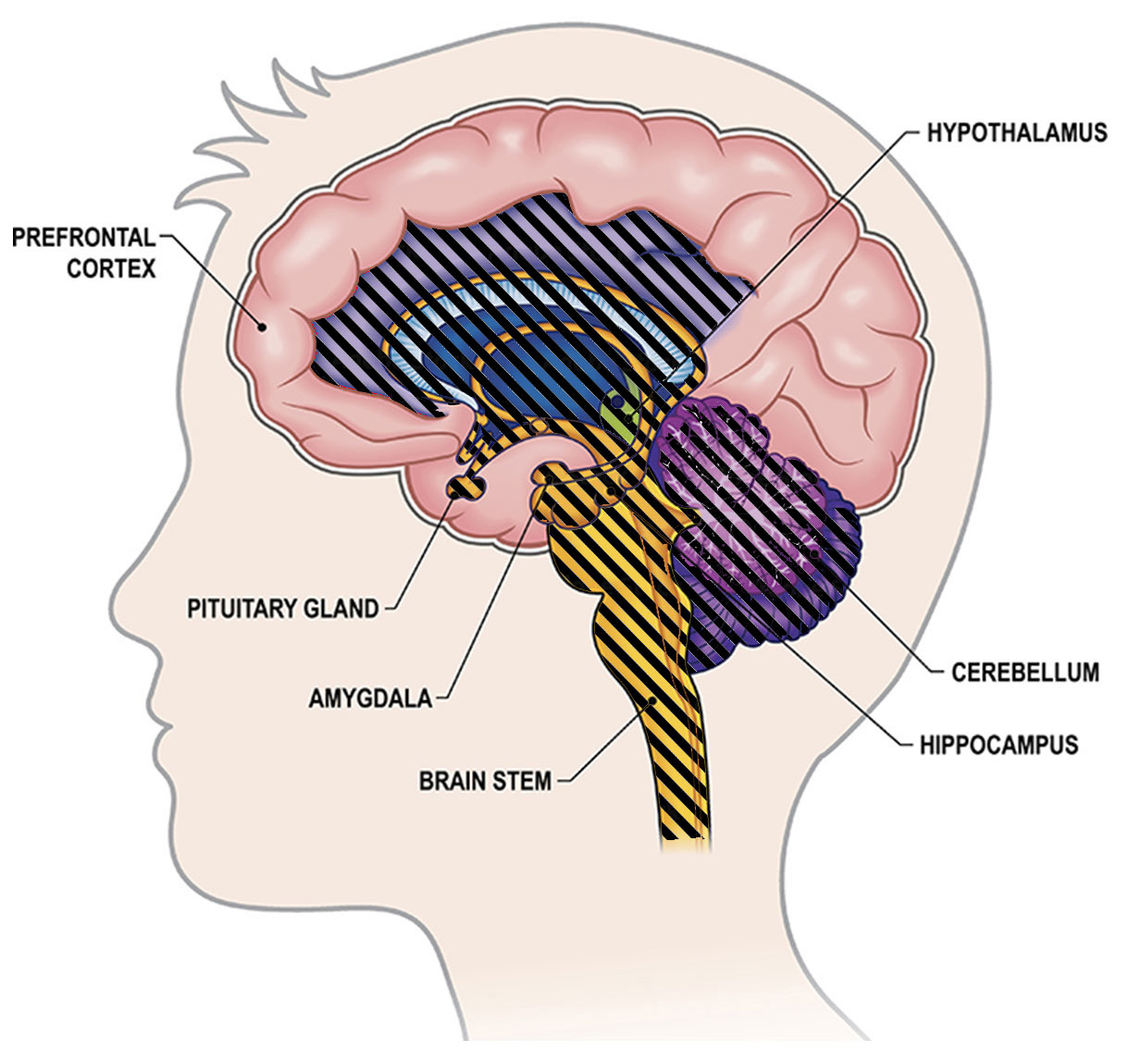
Subcortical structures
The thalamus, which resides just above the hypothalamus, is a subcortical structure that acts as a gateway for sensory information to the cortex.
It plays a crucial role in consciousness by regulating the flow of sensory signals to the neocortex and coordinating the integration of sensory information.
Additionally, the reticular activating system (RAS), located in the brainstem, plays a role in regulating wakefulness and arousal, which are essential components of consciousness.
Most subconscious functions take place in subcortical regions, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus, which play important roles in emotional regulation, memory formation, and instinctual behaviors.
But the subconscious also operates in the neocortex, including procedural memory (e.g., riding a bike) and implicit learning (e.g., picking up social cues).
While subcortical regions play a crucial role in subconscious processes, the entire brain, including the cerebral cortex, can contribute to subconscious mental activities.
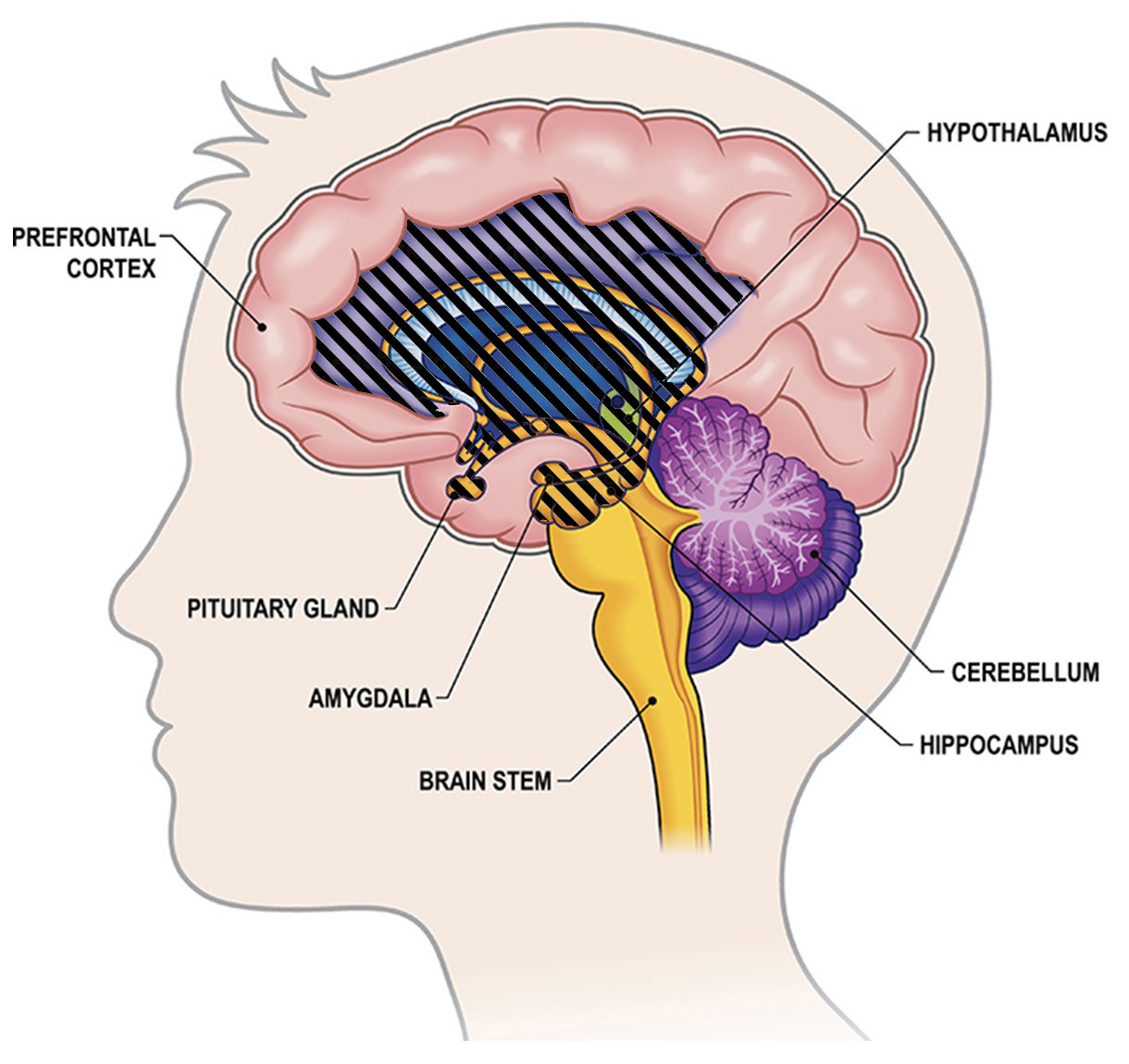
The limbic system
Occasionally, in reference to the subconscious, you will hear the term, “limbic system.” This is a complex set of brain structures involved in emotion, motivation, memory, and behavior regulation.
The limbic system operates mostly in the allocortex and includes the hippocampus, amygdala, thalamus, and hypothalamus.
Although some parts of the limbic system, such as the cingulate cortex, are located in the neocortex, the majority of its components are in the allocortex.
Neuroanatomy Made Ridiculously Simple by the World Federation of Neuroscience Nurses